Weather - short-term atmospheric conditions
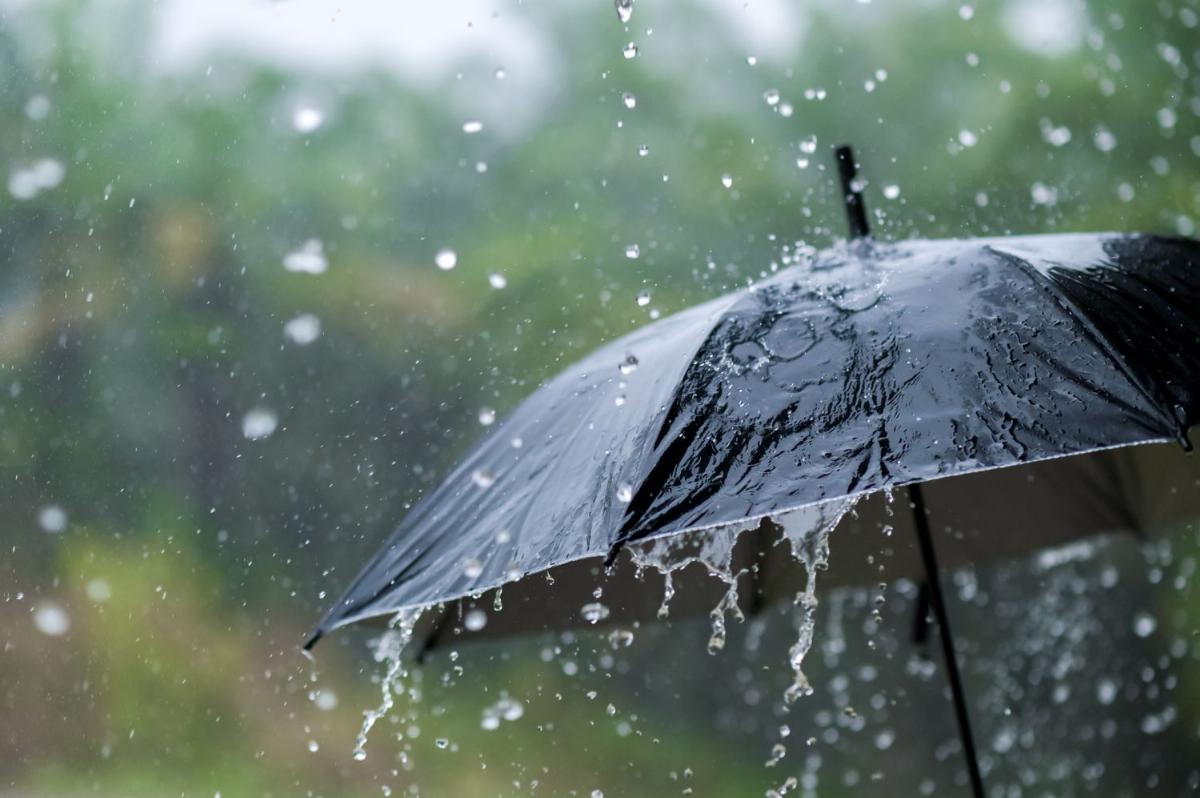
Weather refers to the short-term atmospheric conditions in a specific place at a particular time. It includes various phenomena such as temperature, humidity, precipitation (rain, snow, sleet), wind speed and direction, atmospheric pressure, and visibility. Weather conditions can vary significantly over short periods and across different geographical locations.
Weather is driven by the interactions between the Earth's atmosphere, land, and oceans. Factors such as the Earth's rotation, its tilt, solar radiation, and geographical features (mountains, oceans, etc.) all influence weather patterns. Meteorology is the scientific study of weather, focusing on forecasting and understanding the dynamics of weather systems.
Weather is typically categorized by day-to-day changes, in contrast to climate, which refers to long-term patterns and averages of atmospheric conditions in a region over extended periods (decades or more). Weather phenomena range from everyday conditions, like sunny or cloudy skies, to more extreme events such as thunderstorms, tornadoes, hurricanes, and blizzards.
Weather forecasting is essential for a variety of sectors, including agriculture, transportation, and emergency planning. Modern weather forecasting relies on advanced technologies such as satellites, radar systems, and computer models that analyze data to predict short-term and long-term weather conditions.
Stichworte