US Trade
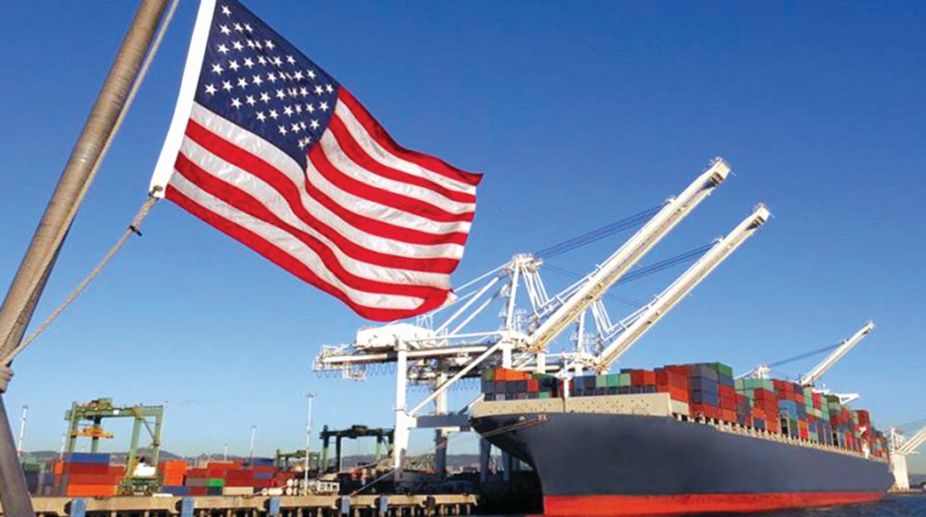
The United States is one of the world’s largest trading nations, engaging in international trade with numerous countries. U.S. trade involves the exchange of goods and services with global markets, and it plays a significant role in the country's economy. The two major components of U.S. trade are imports and exports. The United States imports a wide variety of products, including machinery, vehicles, electronics, pharmaceuticals, and consumer goods, from countries such as China, Canada, Mexico, Japan, and Germany. Key U.S. exports include machinery, aircraft, medical equipment, and agricultural products like soybeans, corn, and wheat, with major trading partners such as China, Canada, and Mexico.
The U.S. has established numerous trade agreements to regulate and facilitate international trade. One of the most significant agreements is the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA), which replaced the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) in 2020. This agreement is designed to create a more balanced trade environment between the U.S., Canada, and Mexico. Other major trade agreements include those with South Korea (KORUS) and the European Union, and ongoing negotiations for further trade partnerships.
The U.S. trade balance, the difference between exports and imports, is an important economic indicator. The U.S. often runs a trade deficit, meaning that it imports more than it exports. In recent years, the trade deficit has been particularly high with countries like China, prompting discussions about tariffs and trade policies aimed at reducing the gap. The U.S. government, through the Office of the United States Trade Representative (USTR), plays a critical role in shaping trade policy, negotiating agreements, and addressing disputes.
International organizations like the World Trade Organization (WTO) oversee the rules of international trade, and the U.S. is a key member. The U.S. trade system also involves various government bodies, including the U.S. Department of Commerce and the U.S. International Trade Commission, which handle aspects like trade enforcement, compliance, and economic data collection.
Trade policies are regularly debated within the U.S., with issues like tariffs, trade deficits, and global competition frequently discussed. These policies have wide-reaching effects on industries, consumers, and the overall economy. U.S. trade impacts sectors from manufacturing and technology to agriculture and energy.
Stichworte
Quellen