Tehran
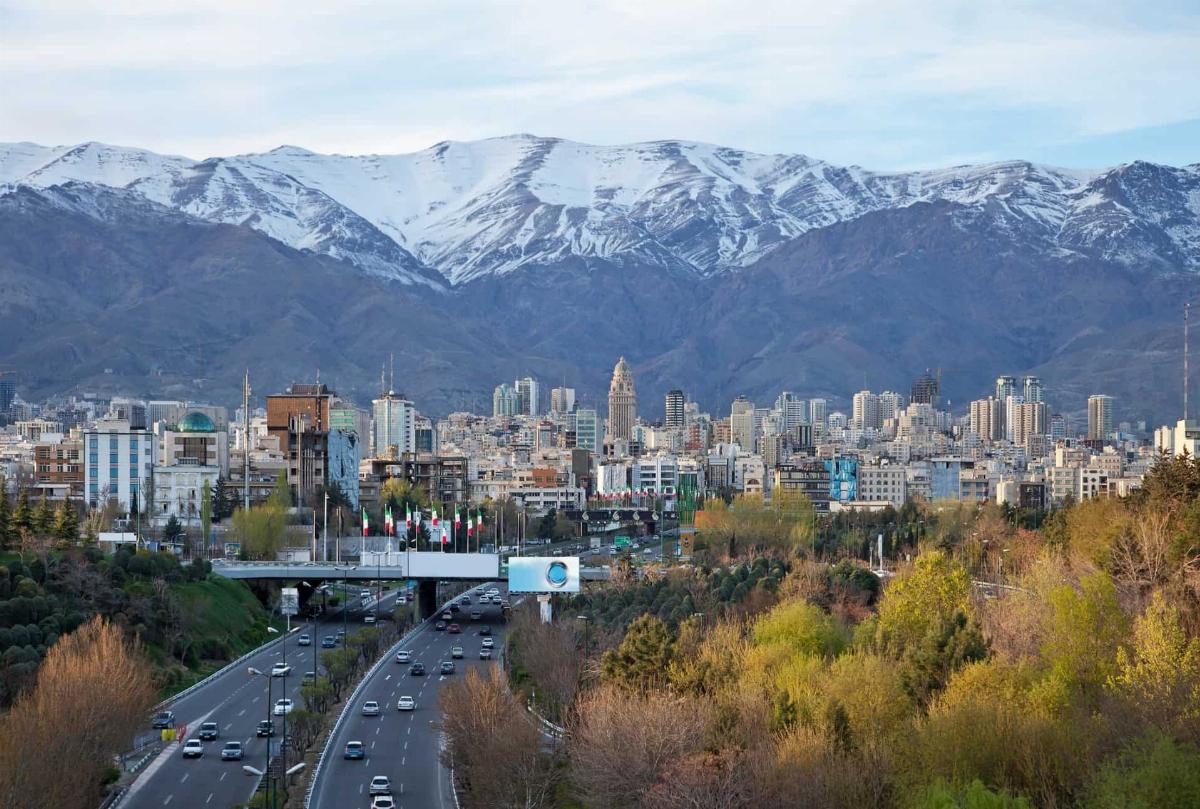
Tehran is the capital and largest city of Iran, located in the northern part of the country near the southern slopes of the Alborz mountain range. As of 2021, Tehran’s metropolitan area has a population of over 13 million, making it one of the most populous cities in Western Asia. Tehran serves as the political, economic, and cultural center of Iran. The city was first established as the capital in 1796 by Agha Mohammad Khan of the Qajar dynasty, and it has remained the country’s capital ever since.
Tehran is known for its modern infrastructure, with numerous highways, large buildings, and a mix of contemporary and historical architecture. The city houses key government institutions, including the offices of the Supreme Leader and the President of Iran, as well as the Iranian Parliament. The city is also home to many embassies, making it a hub for international diplomacy within the region.
Economically, Tehran is the heart of Iran's industrial and commercial activities. The city has a thriving economy, with industries such as textiles, construction, electronics, and chemicals playing a significant role. Tehran is also an important center for the Iranian oil and gas industry. The Tehran Stock Exchange is the largest in the country and plays a critical role in the nation’s economy.
Tehran’s climate varies, with hot summers and cold winters, influenced by its proximity to the mountains and desert areas. The city faces significant environmental challenges, particularly air pollution and traffic congestion, due to its dense population and high number of vehicles. Efforts to address these issues include expanding public transportation, such as the Tehran Metro and bus systems.
Tehran is also home to several universities and cultural institutions, including the University of Tehran, one of the most prestigious universities in Iran. The city is known for its museums, such as the National Museum of Iran and the Golestan Palace, a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Stichworte
Quellen