Supreme Court
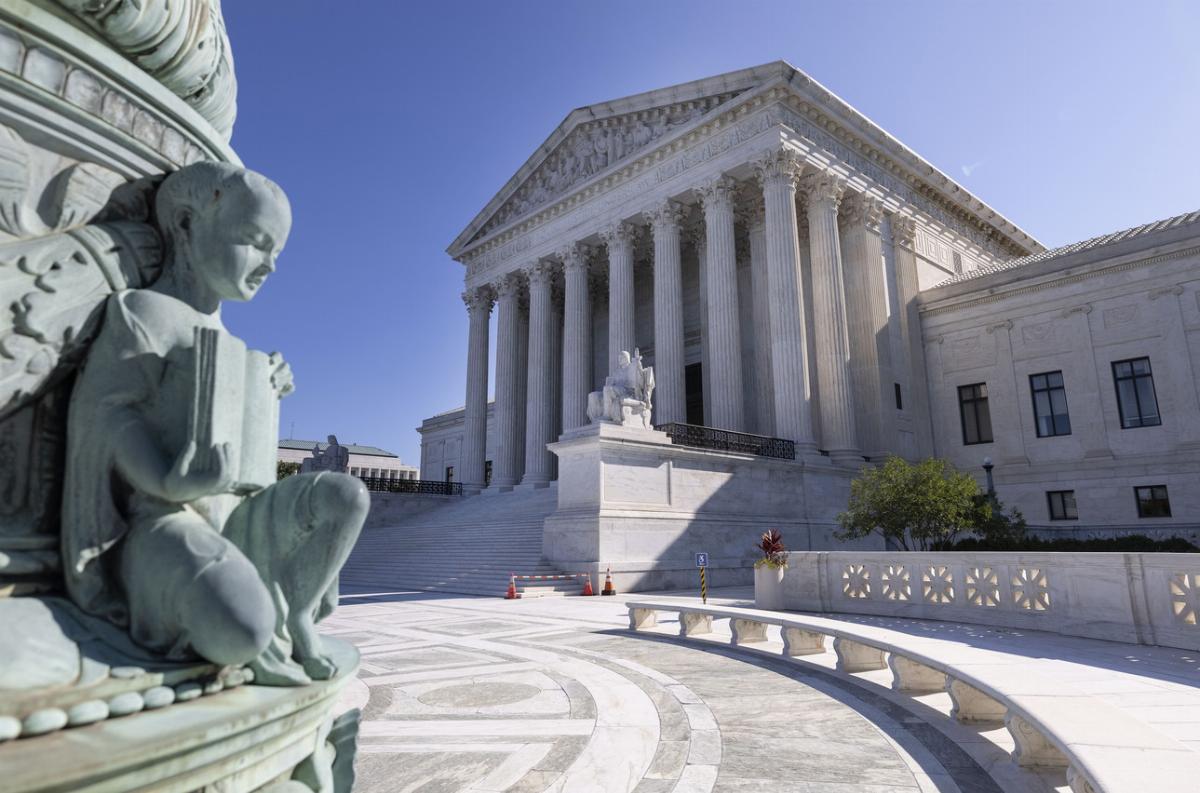
The Supreme Court of the United States is the highest judicial authority in the country. Established by Article III of the U.S. Constitution in 1789, the Court has ultimate jurisdiction over all federal and state courts and serves as the final arbiter of constitutional issues. It consists of nine justices, including one Chief Justice and eight Associate Justices, who are nominated by the President and confirmed by the Senate. Justices hold their positions for life, unless they resign, retire, or are impeached and removed.
The Supreme Court’s primary role is to interpret the U.S. Constitution and to review the constitutionality of laws passed by Congress and state legislatures. It also hears appeals from lower courts on a wide range of issues, including civil rights, free speech, criminal law, and federal regulations. Cases can reach the Supreme Court through a process called "writ of certiorari," in which parties petition the Court to review decisions made by lower courts. However, the Court hears only a small percentage of the thousands of petitions it receives each year.
Notable decisions by the Supreme Court have shaped American law and society. Key rulings include Marbury v. Madison (1803), which established the principle of judicial review, allowing the Court to strike down unconstitutional laws; Brown v. Board of Education (1954), which ended racial segregation in public schools; and Roe v. Wade (1973), which protected a woman’s right to choose an abortion, though this decision was overturned in Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization (2022). Other significant rulings address issues such as same-sex marriage, gun rights, and healthcare.
The ideological composition of the Supreme Court can shift with each new appointment, reflecting broader political and social changes in the country. Over time, the Court has become a focal point of political debate, with its decisions affecting issues of national importance. Public interest in the nomination and confirmation of justices is often heightened due to the Court’s significant role in shaping U.S. law.
Stichworte
Quellen