Morocco
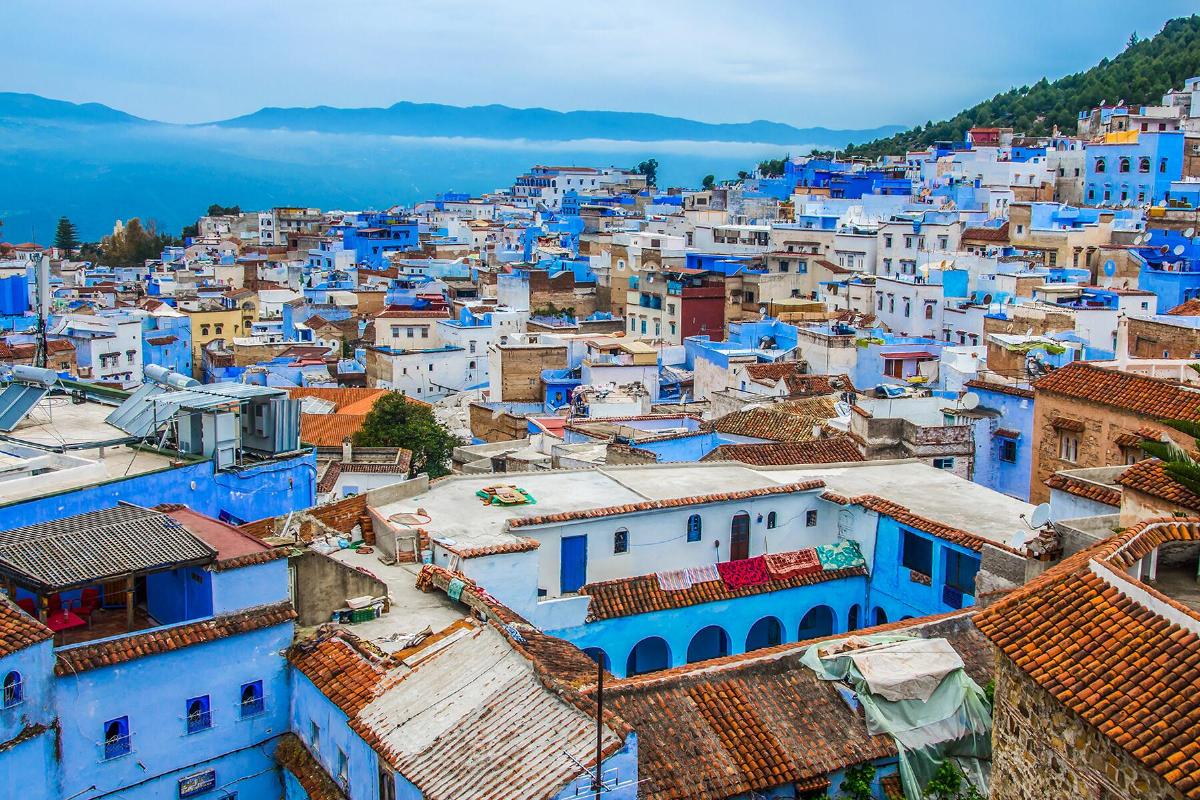
Morocco is a North African country bordered by the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea, with a population of over 37 million people. Its capital is Rabat, while the largest city and economic center is Casablanca. The official languages are Arabic and Berber, with French widely used in business, government, and diplomacy. Morocco has a rich history, dating back to ancient Berber kingdoms and later influenced by Phoenicians, Carthaginians, and Romans. In the 7th century, Arab expansion introduced Islam, which became the dominant religion.
The country experienced several dynastic shifts, including the Idrisid, Almoravid, and Almohad empires, all of which played key roles in shaping its cultural and architectural heritage. In 1912, Morocco became a French and Spanish protectorate but regained independence in 1956. Its political system is a constitutional monarchy with King Mohammed VI as the head of state since 1999. Morocco’s economy is diverse, with sectors such as agriculture, mining, and tourism contributing significantly. It is one of the world's largest producers of phosphates.
Tourism is a major industry, with attractions like the imperial cities of Marrakech, Fez, and Meknes, the Atlas Mountains, and the Sahara Desert. The country's cuisine, known for dishes like tagine and couscous, is internationally renowned. Morocco is also a significant player in African and Arab League politics and maintains close relations with Europe, particularly France and Spain.
Morocco is a member of international organizations such as the United Nations and the African Union and has advanced human rights and economic reforms over the last few decades. The country is recognized for its stability and has played a pivotal role in promoting peace efforts in the region.
Stichworte