Lebanon
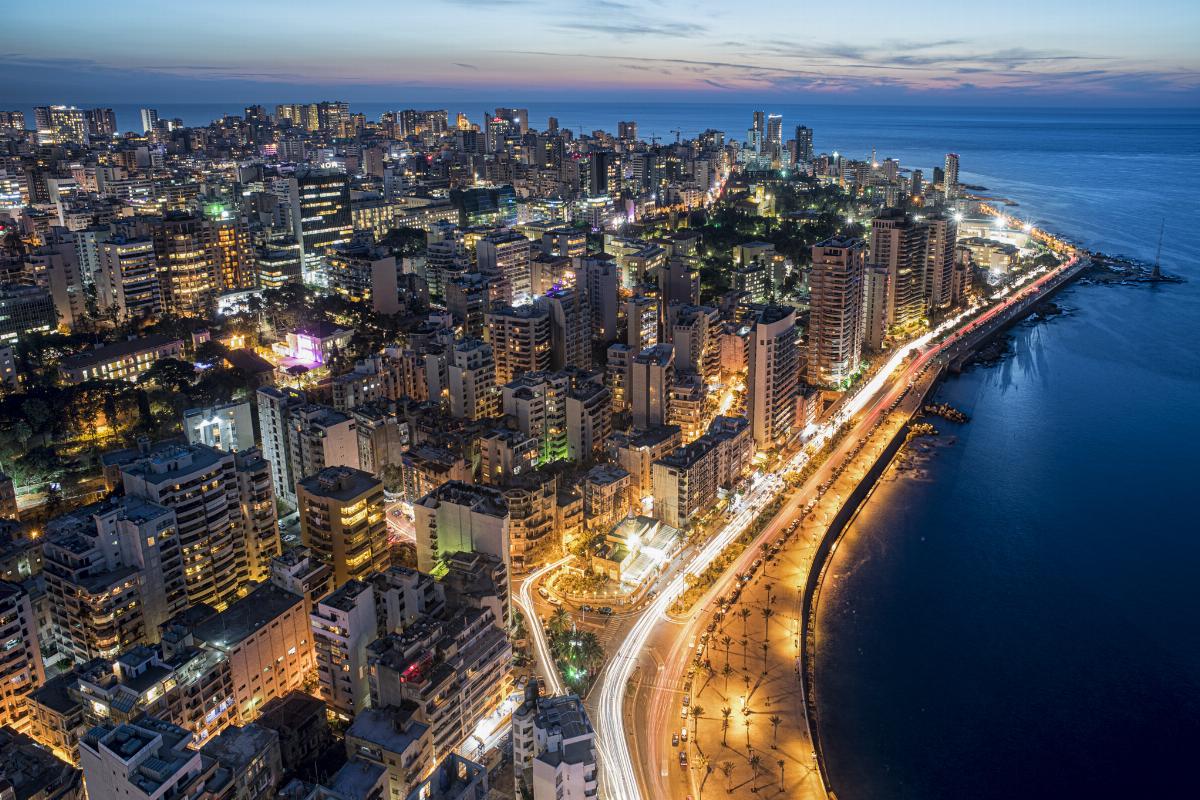
Lebanon is a country located on the eastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea in the Middle East. It is bordered by Syria to the north and east, Israel to the south, and the Mediterranean to the west. Lebanon has a population of approximately 6.8 million people and covers an area of about 10,452 square kilometers. The official language is Arabic, though French and English are also widely spoken. Beirut is the capital and largest city of the country. Lebanon's geography is characterized by its mountainous terrain, with the Mount Lebanon range running parallel to the coast, and the fertile Bekaa Valley lying between the mountains and Syria.
Lebanon has a rich cultural history that reflects its location at the crossroads of various civilizations. The area was historically home to the Phoenicians, an ancient Semitic-speaking people known for their maritime trading empire. Over the centuries, Lebanon has been influenced by various empires, including the Assyrian, Persian, Roman, Byzantine, and Ottoman empires. Lebanon became an independent country in 1943, following a period of French mandate after World War I.
The country's political system is unique, based on confessionalism, which distributes political power among its religious communities, with the presidency reserved for a Maronite Christian, the prime ministership for a Sunni Muslim, and the speaker of parliament for a Shia Muslim. This system aims to maintain balance between the various religious groups, but it has also been a source of tension throughout Lebanon’s modern history.
Lebanon's civil war, which lasted from 1975 to 1990, was one of the most significant events in the country's history, leading to the deaths of over 120,000 people and the displacement of many more. The war involved numerous factions, including religious groups, Palestinian factions, and international actors such as Israel and Syria. Since the end of the civil war, Lebanon has faced multiple challenges, including political instability, foreign interventions, and economic crises.
The country's economy is heavily based on the services sector, particularly banking and tourism. Historically, Beirut was known as the "Paris of the Middle East" due to its vibrant cultural and social scene. However, in recent years, Lebanon has experienced a severe economic crisis, exacerbated by political corruption, the Syrian refugee crisis, and the COVID-19 pandemic. The Beirut port explosion in August 2020 was another major setback, causing widespread devastation in the capital.
Lebanon has a diverse religious makeup, with Islam and Christianity being the dominant faiths. Sunni and Shia Muslims, Maronite Christians, Greek Orthodox Christians, and Druze make up the major religious communities. This diversity has shaped Lebanon’s cultural and social life, but it has also been a source of political conflict.
Stichworte
Quellen