Food Prices
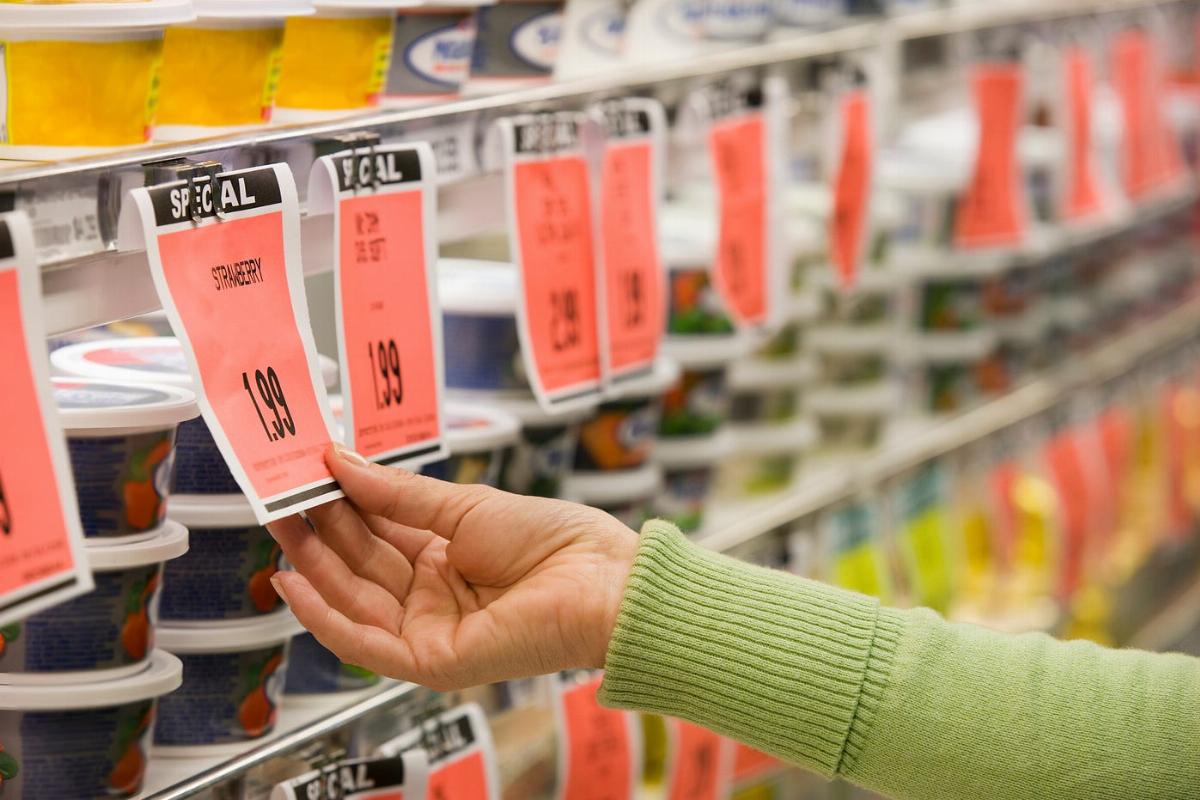
Food prices are determined by various factors, including supply and demand, production costs, weather conditions, trade policies, and global economic conditions. In recent years, food prices have been affected by a combination of inflation, supply chain disruptions, and changing consumer demand. These factors have contributed to price increases for various staple foods, such as grains, dairy products, meat, and fresh produce.
Global food prices are influenced by agricultural production and input costs. Key inputs, such as fertilizers, fuel, and labor, impact the cost of producing food. When input costs rise, farmers and food producers often pass these costs on to consumers, resulting in higher retail prices. Weather conditions, such as droughts, floods, and storms, can also reduce crop yields and livestock production, leading to reduced supply and higher prices.
Trade policies and international relations affect food prices, as countries that rely on food imports are vulnerable to fluctuations in global markets. Trade restrictions, tariffs, and sanctions can impact the availability of imported food products, while global demand for certain commodities can drive up prices. The COVID-19 pandemic created additional disruptions in the global food supply chain, affecting everything from production and transportation to retail.
Consumer demand plays a role in shaping food prices. Economic growth in emerging markets has increased demand for meat, dairy, and processed foods, placing pressure on the global food supply. At the same time, changing consumer preferences, such as the demand for organic and sustainably sourced foods, have affected food pricing structures.
Governments and international organizations, such as the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the World Bank, monitor food prices to address food security concerns, especially in low-income countries where rising food costs can lead to hunger and malnutrition. These organizations often provide assistance and implement policies aimed at stabilizing food prices and ensuring affordable access to basic foods.
Stichworte
Quellen